Out of Africa

Did creation begin in Africa?
Paleontology
Human Migration
Ancient Civilizations

In the News ...

Following Genetic Footprints out of Africa: First Modern Humans Settled in Arabia
Science Daily - January 27, 2012

A new study, using genetic analysis to look for clues about human migration over sixty thousand years ago, suggests that the first modern humans settled in Arabia on their way from the Horn of Africa to the rest of the world. Using mitochondrial DNA analysis, which traces the female line of descent and is useful for comparing relatedness between different populations, the researchers compared complete genomes from Arabia and the Near East with a database of hundreds more samples from Europe. They found evidence for an ancient ancestry within Arabia.
Trail of 'Stone Breadcrumbs' Reveals the Identity of One of the First Human Groups to Leave Africa Science Daily - December 1, 2011
These new findings challenge long-held assumptions about the timing and route of early human expansion out of Africa. Using a technique called Optically Stimulated Luminescence (OSL) to date one of the sites in Oman, researchers have determined that Nubian MSA toolmakers had entered Arabia by 106,000 years ago, if not earlier. This date is considerably older than geneticists have put forth for the modern human exodus from Africa, who estimate the dispersal of our species occurred between 70,000 and 40,000 years ago. Even more surprising, all of the Nubian MSA sites were found far inland, contrary to the currently accepted theory that envisions early human groups moving along the coast of southern Arabia.
All Non-Africans Part Neanderthal, Genetics Confirm Discovery - July 18, 2011
If your heritage is non-African, you are part Neanderthal, according to a new study in the July issue of Molecular Biology and Evolution. Discovery News has been reporting on human/Neanderthal interbreeding for some time now, so this latest research confirms earlier findings. Damian Labuda of the University of Montreal's Department of Pediatrics and the CHU Sainte-Justine Research Center conducted the study with his colleagues. They determined some of the human X chromosome originates from Neanderthals, but only in people of non-African heritage. "This confirms recent findings suggesting that the two populations interbred," Labuda was quoted as saying in a press release.
New algorithm provides new insights into evolutionary exodus out of Africa PhysOrg - July 14, 2011
Researchers have probed deeper into human evolution by developing an elegant new technique to analyze whole genomes from different populations. One key finding from the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute's study is that African and non-African populations continued to exchange genetic material well after migration out-of-Africa 60,000 years ago. This shows that interbreeding between these groups continued long after the original exodus.
'Mitochondrial Eve' Research: Humanity Was Genetically Divided For 100,000 Years Science Daily - May 16, 2008
The human race was divided into two separate groups within Africa for as much as half of its existence, says a Tel Aviv University mathematician. Climate change, reduction in populations and harsh conditions may have caused and maintained the separation.
Massive Genetic Study Supports "Out of Africa" Theory National Geographic - February 21, 2008
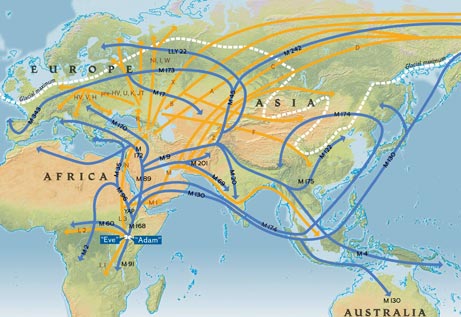
Two big genetic studies confirm theories that modern humans evolved in Africa and then migrated through Europe and Asia to reach the Pacific and Americas.
Geologists Say 'Wall Of Africa' Allowed Humanity To Emerge Science Daily - December 22, 2007
Scientists long have focused on how climate and vegetation allowed human ancestors to evolve in Africa. Now, University of Utah geologists are calling renewed attention to the idea that ground movements formed mountains and valleys, creating environments that favored the emergence of humanity.
First modern humans emigrated along Africa coast BBC - May 13, 2005

The first humans who left Africa to populate the world headed south along the coast of the Indian Ocean, Science magazine reports. Scientists had always thought the exodus from Africa around 70,000 years ago took place along a northern route into Europe and Asia. But according to a genetic study, early modern humans followed the beach, possibly lured by a seafood diet. They quickly reached Australia but took much longer to settle in Europe.
Ancient African Skies Space.com - April 7, 2005
"Bwana! That must be it!" I pointed back over my right shoulder at some man-sized stone pillars off on a rise from the dirt road we were driving on. The road would be described by Kenyans as "corrugated" meaning that we had to get out in some places to look for it on our way to the Turkana region--not too far from where the most ancient hominid fossils had been found by Richard Leakey, Director of the National Museums.
We had heard of an ancient astronomy site in this region made up of basalt pillars that were magnetic, so needed to be remeasured using something other than compasses. Eddie Frank, of the Tusker Trail Company, some students from various places in the U.S., and I had come to do just that. We had camped with hippos at Lake Nivasha, swum in Lake Turkana known to have over 3 million crocodiles in it, watched as several million pink flamingos had taken to the air around Lake Nakuru, and seen the migration of a couple million wildebeests across the Masaai Mara plains, all on our roundabout safari to this ancient astronomy site.
The pillars were known as "Namoratunga" or "stone people" in the Turkana language. They had been said to have been built for an astronomical purpose, to reckon the Borana calendar, and were reputed to be a couple of thousand years old. They had petroglyphs on them, some matching the ancient property symbols of the Kush, a people of the Sudan who had once conquered Egypt (in the 8th Century B.C.) and whose language has yet to be deciphered. From maps of ancient Kush, I knew that the front of almost all their pyramids appeared to face the star Sirius, which has not changed its position in the sky very much for the last several thousand years.
We had a description of the Borana calendar, but this did not make astronomical sense. For example, the new year of the Borana calendar was said to occur when the star beta Triangulum was "in conjunction" with the new moon (new, give or take a couple of days). A new moon is, of course, close to the sun (i.e., a thin crescent), and consequently found in the twilight sky. However, the star beta Triangulum is a 3rd magnitude star and could not been seen in twilight. Thus, we could not even get the Borana new year started according to the description we had from anthropologists.
Fossils Shed Light on Africa's "Missing Years" National Geographic - December 3, 2003
A massive, ancient, rhino-like creature with two bony horns protruding from its nose and several species of distant elephant relatives are among a jackpot of fossils recovered from the highlands of Ethiopia. The fossils help fill a huge gap in the evolutionary history of African mammals known as the "missing years," shedding light on the origin and distribution of the famed beasts that roam Africa today.
Oldest skull found in Ethiopia - 2 adult males - 1 child BBC - June 11, 2003
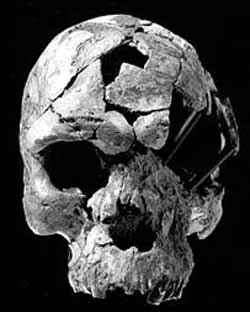
Three fossilized skulls unearthed in Ethiopia are said by scientists to be among the most important discoveries ever made in the search for the origin of humans. The crania of two adults and a child, all dated to be around 160,000 years old, were pulled out of sediments near a village called Herto in the Afar region in the east of the country. They are described as the oldest known fossils of modern humans, or Homo sapiens. What excites scientists so much is that the specimens fit neatly with the genetic studies that have suggested this time and part of Africa for the emergence of mankind.
160,000-Year-Old Fossilized Skulls From Ethiopia Are Oldest Modern Humans Science Daily - June 12, 2003

He may have looked like this...
Three fossilized skulls unearthed in Herto, Ethiopia are said by scientists to be among the most important discoveries ever made in the search for the origin of humans. The fossilized skulls of two adults and one child discovered in the Afar region of eastern Ethiopia have been dated at 160,000 years, making them the oldest known fossils of modern humans, or Homo sapiens. The skulls, dug up near a village called Herto, fill a major gap in the human fossil record, an era at the dawn of modern humans when the facial features and brain cases we recognize today as human first appeared. The fossils date precisely from the time when biologists using genes to chart human evolution predicted that a genetic "Eve" lived somewhere in Africa and gave rise to all modern humans.
Tanzania, Ethiopia origin for humans BBC - April 2, 2003

New DNA evidence suggests "African Eve", the 150,000-year-old female ancestor of every person on Earth, may have lived in Tanzania or Ethiopia. A genetic study has shown that the oldest known human DNA lineages are those of East Africans. The most ancient populations include the Sandawe, Burunge, Gorowaa and Datog people who live in Tanzania. Researchers found a very high amount of genetic variation, or diversity, between the mitochondrial DNA of different individuals in these populations. Mitochondrial DNA is passed down exclusively through the maternal line. The longer a population has existed, the more variation accumulates in its DNA lineages."They are showing really deep, old lineages with lots of diversity. They appear to be the oldest lineages identified in Africa to date," said Dr Sarah Tishkoff, of the University of Maryland, US, who led the research.

African Creation Myths

Despite their differences, these four stories do share the belief that they were created by a god. While they vary in their description of how this occurred and why, they all serve the same purpose. Through their explanation of how this occurred, one can see what they view their place in the world to be. By answering their questions, these stories served as both a comforting basis for the African people and a way of connecting to future generations. As such, these tales of creation are works of truly great literature.


First Kaang created a wondrous tree, with branches stretching over the entire country. At the base of the tree he dug a hole that reached all the way down into the world where the people and animals lived. After he had finished furnishing the world as he pleased he led the first man up the hole.
He sat down on the edge of the hole and soon the first woman came up out of it. Soon all the people were gathered at the foot of the tree, awed by the world they had just entered. Next, Kaang began helping the animals climb out of the hole. In their eagerness some of the animals found a way to climb up through the tree's roots and come out of the branches. They continued racing out of the world beneath until all of the animals were out.
Kaang gathered all the people and animals about him. He instructed them to live together peacefully. Then he turned to the men and women and warned them not to build any fires or a great evil would befall them. They gave their word and Kaang left to where he could watch his world secretly.
As evening approached the sun began to sink beneath the horizon. The people and animals stood watching this phenomenon, but when the sun disappeared fear entered the hearts of the people. They could no longer see each other as they lacked the eyes of the animals which were capable of seeing in the dark. They lacked the warm fur of the animals also and soon grew cold. In desperation one man suggested that they build a fire to keep warm. Forgetting Kaang's warning they disobeyed him. They soon grew warm and were once again able to see each other.
However the fire frightened the animals. They fled to the caves and mountains and ever since the people broke Kaang's command people have not been able to communicate with animals.
Now fear has replaced the seat friendship once held between the two groups.The Bushmen of Africa believe that not only are plants and animals alive, but also rain, thunder, the wind, spring, etc. They claim:What we see is only the outside form or body. Inside is a living spirit that we cannot see. These spirits can fly out of one body into another. For example, a woman's spirit might sometime fly into a leopard; or a man's spirit fly into a lion's body. (Fahs and Spoerl 6) This may be part of the reason that animals play such an important role in their myth.
Khoisan Religion Wikipedia

 Dogon Their Creation Gods the Nommo came from Sirius
Dogon Their Creation Gods the Nommo came from Sirius


Egyptian Gods and Goddesses
Ancient Egyptian creation myths are the ancient Egyptian accounts of the creation of the world. The Pyramid Texts, tomb wall decorations and writings, dating back to the Old Kingdom (2780 - 2250 B.C.E) have given us most of our information regarding early Egyptian creation myths. These myths also form the earliest religious compilations in the world. The ancient Egyptians had many creator gods and associated legends. Thus the world or more specifically Egypt was created in diverse ways according to different parts of the country.
In all of these myths, the world was said to have emerged from an infinite, lifeless sea when the sun rose for the first time, in a distant period known as zp tpj, "the first occasion". Different myths attributed the creation to different gods: the set of eight primordial deities called the Ogdoad, the self-engendered god Atum and his offspring, the contemplative deity Ptah, and the mysterious, transcendent god Amun. While these differing cosmogonies competed to some extent, in other ways they were complementary, as different aspects of the Egyptian understanding of creation.
The different creation myths had some elements in common. They all held that the world had arisen out of the lifeless waters of chaos, called Nu. They also included a pyramid-shaped mound, called the benben, which was the first thing to emerge from the waters. These elements were likely inspired by the flooding of the Nile River each year; the receding floodwaters left fertile soil in their wake, and the Egyptians may have equated this with the emergence of life from the primeval chaos. The imagery of the pyramidal mound derived from the highest mounds of earth emerging as the river receded.
The sun was also closely associated with creation, and it was said to have first risen from the mound, as the general sun-god Ra or as the god Khepri, who represented the newly-risen sun. There were many versions of the sun's emergence, and it was said to have emerged directly from the mound or from a lotus flower that grew from the mound, in the form of a heron, falcon, scarab beetle, or human child.
Another common element of Egyptian cosmogonies is the familiar figure of the cosmic egg, a substitute for the primeval waters or the primeval mound. One variant of the cosmic egg version teaches that the sun god, as primeval power, emerged from the primeval mound, which itself stood in the chaos of the primeval sea.
Cosmogonies
The different creation accounts were each associated with the cult of a particular god in one of the major cities of Egypt: Hermopolis, Heliopolis, Memphis, and Thebes. To some degree these myths represent competing theologies, but they also represent different aspects of the process of creation.
The creation myth promulgated in the city of Hermopolis focused on the nature of the universe before the creation of the world. The inherent qualities of the primeval waters were represented by a set of eight gods, called the Ogdoad. The god Nu and his female counterpart Naunet represented the inert primeval water itself; Huh and his counterpart Hauhet represented the water's infinite extent; Kuk and Kauket personified the darkness present within it; and Amun and Amaunet represented its hidden and unknowable nature, in contrast to the tangible world of the living. The primeval waters were themselves part of the creation process, therefore, the deities representing them could be seen as creator gods.
According to the myth, the eight gods were originally divided into male and female groups. They were symbolically depicted as aquatic creatures because they dwelt within the water: the males were represented as frogs, and the females were represented as snakes. These two groups eventually converged, resulting in a great upheaval, which produced the pyramidal mound. From it emerged the sun, which rose into the sky to light the world.
Heliopolis
In Heliopolis, the creation was attributed to Atum, a deity closely associated with Ra, who was said to have existed in the waters of Nu as an inert potential being. Atum was a self-engendered god, the source of all the elements and forces in the world, and the Heliopolitan myth described the process by which he "evolved" from a single being into this multiplicity of elements. The process began when Atum appeared on the mound and gave rise the air god Shu and his sister Tefnut, whose existence represented the emergence of an empty space amid the waters. To explain how Atum did this, the myth uses the metaphor of masturbation, with the hand he used in this act representing the female principle inherent within him.
He is also said to have to have "sneezed" and"spat" to produce Shu and Tefnut, a metaphor that arose from puns on their names. Next, Shu and Tefnut coupled to produce the earth god Geb and the sky goddess Nut, who defined the limits of the world. Geb and Nut in turn gave rise to four children, who represented the forces of life: Osiris, god of fertility and regeneration; Isis, goddess of motherhood; Set, the god of male sexuality; and Nephthys, the female complement of Set. The myth thus represented the process by which life was made possible. These nine gods were grouped together theologically as the Ennead, but the eight lesser gods, and all other things in the world, were ultimately seen as extensions of Atum.
Memphis
The Memphite version of creation centered on Ptah, who was the patron god of craftsmen. As such, he represented the craftsman's ability to envision a finished product, and shape raw materials to create that product. The Memphite theology said that Ptah created the world in a similar way. This, unlike the other Egyptian creations, was not a physical but an intellectual creation by the Word and the Mind of God. The ideas developed within Ptah's heart (regarded by the Egyptians as the seat of human thought) were given form when he named them with his tongue. By speaking these names, Ptah produced the gods and all other things.
The Memphite creation myth coexisted with that of Heliopolis, as Ptah's creative thought and speech were believed to have caused the formation of Atum and the Ennead. Ptah was also associated with Tatjenen, the god who personified the pyramidal mound.
Thebes
Theban theology claimed that Amun was not merely a member of the Ogdoad, but the hidden force behind all things. There is a conflation of all notions of creation into the personality of Amun, a synthesis which emphasizes how Amun transcends all other deities in his being Òbeyond the sky and deeper than the underworldÓ. One Theban myth likened Amun's act of creation to the call of a goose, which broke the stillness of the primeval waters and caused the Ogdoad and Ennead to form.
Amun was separate from the world, his true nature was concealed even from the other gods. At the same time, however, because he was the ultimate source of creation, all the gods, including the other creators, were in fact merely aspects of Amun. Amun eventually became the supreme god of the Egyptian pantheon because of this belief.
Amun is synonymous with the growth of Thebes as a major religious capital. But it is the columned halls, obelisks, colossal statues, wall-reliefs and hieroglyphic inscriptions of the Theban temples that we look to gain the true impression of AmunÕs superiority. Thebes was thought of as the location of the emergence of the primeval mound at the beginning of time.



Before long, Fam grew arrogant, he mistreated the animals and stopped worshipping Nzame. Nzame, angered, brought forth thunder and lightning and destroyed everything that was, except Fam, who had been promised immortality. Nzame, in his three aspects, decided to renew the earth and try again. He applied a new layer of earth to the planet, and a tree grew upon it.
The tree dropped seeds which grew into more trees. Leaves that dropped from them into the water became fish, those that dropped on land became animals. The old parched earth still lies below this new one, and if one digs deep enough it can be found in the form of coal. Nzame made a new man, one who would know death, and called him Sekume. Sekume fashioned a woman, Mbongwe, from a tree. These people were made with both Gnoul (body) and Nissim (soul). Nissim gives life to Gnoul. When Gnoul dies, Nissim lives on. They produced many children and prospered.

Many of the creation accounts tell of Mawu creating everything as she was carried from place to place on the back or in the mouth of Aido Hwedo, the rainbow serpent. The earth was created first, its curves, slopes and rises shaped by the winding, snaking motions of Aido Hwedo. Mountains formed from Aido Hwedo's excrement wherever they stopped to rest, leaving precious minerals inside. When Mawu finished, all of the mountains, trees, elephants and other creations left world too heavy, so she asked Aido Hwedo to coil, to encircle the earth and rest underneath to support its weight.
Aido Hwedo holds his own tail in his mouth to hold fast to the earth, and rests in the cool of the seas which Mawu made for him to protect him from the heat. Mawu's son, Agbe, now commands them. Whenever Aido Hwedo shifts or readjusts his position, he causes an earthquake or tidal wave.

Ggulu was not pleased, but blessed the marriage after Nambi had persuaded him. Ggulu advised Kintu and Nambi to leave heaven secretly, so that Walumbe, one of Nambi's brothers would not find out about the marriage until they had left. It was feared that Walumbe (which means "that which causes sickness and death") would insist on going with them and bring them misery.
Kintu and Nambi set out for earth the next morning, taking with them the few things that Nambi packed, and her chicken. While they were descending, Nambi remembered that she had forgotten to bring the millet that her chicken would feed on. Kintu tried to persuade her not to return to fetch the millet, but she left him and returned to fetch the millet. On the way back from fetching the millet, she met Walumbe. She did not tell him where she was going, but filled with curiosity, Walumbe insisted on going with her. Kintu and Nambi were therefore forced to go to earth together with Walumbe.
Walumbe's presence on earth caused suffering and conflicts. That, according to the legend, is how sickness and death started. The area where Walumbe is traditionally thought to have fallen to earth and to have hidden from Ggulu is the Tanda Pits, west of Kampala on the south side of the road to the town of Mityana.

Then Mangala made three more pairs of seeds, and each pair became the four elements, the four directions, as corners in the framework of the world's creation. This he folded into a hibiscus seed. The twin pairs of seeds, which are seen as having opposite sex, are referred to as the egg or placenta of the world. This egg held an additional two pairs of twins, one male and one female, who were the archetype of people.
Among them was Pemba who wished to dominate and so he left the egg early, ripping a piece of his placenta. Pemba fell through space and his torn placenta became the earth. Because he left the egg prematurely the earth formed from this piece was arid and barren and of no use to Pemba. So Pemba tried to return to the egg, to rejoin his twin and his place in the rest of the placenta.
But it was not to be found-Mangala had changed the remaining placenta into the sun. So Pemba stole male seeds from Mangala's clavicle, and took them to the barren earth and planted them there. Only one of them could germinate in the dry earth, a male eleusine seed which grew in the blood of the placenta. But because Pemba had stolen the seed and it germinated in Pemba's own placenta, the earth became impure and the eleusine seed turned red.
Faro, the other male twin, who had assumed the form of twin fish, was sacrificed to atone for Pemba and purify the earth. Faro was cut into sixty pieces which fell to the earth where they became trees. Mangala restored Faro to life giving him now the form of a human, and sent him down to earth in an ark made from his placenta. With him came four pairs of male and four pairs of female twins who became the original ancestors of mankind, all made from Faro's placenta. The ark also held all the animals and plants, which also carried the male and female life force. Sourakata followed with the first sacred drum made of the sacrificed Faro's skull which he played to bring rain. When the rain did not come, the ancestral smith came to earth and with his hammer, he struck a rock and then the rain came.
Faro created all the world that mankind has come to know from the descendants of Mangala's original egg seeds. He caused the land to flood to wash away the impure seed of his brother, Pemba. From this flood, only the good were saved, sheltered by Faro's ark.

The story of Mbombo's creation tells that in the beginning, Mbombo was alone, and darkness and water covered the all earth. It would happen that Mbombo came to feel an intense pain in his stomach, and then Mbombo vomited the sun, the moon, and stars. The heat and light from the sun evaporated the water covering the earth, creating clouds, and after time, the dry hills emerged from the water. Then Mbombo vomited once more, bringing forth nine animals: the leopard, called Koy Bumba; the eagle, Ponga Bumba; the crocodile, Ganda Bumba; the fish, Yo Bumba; the tortoise, Kono Bumba; a black leopard-like animal, Tsetse Bumba; a white heron, Nyanyi Bumba; a scarab; and a goat named Budi. Mbombo also vomited many men, one of them all white like himself who is called Loko Yima.
These nine animals went on to create all the world's creatures. The heron created all flying birds but one, the kite, and the crocodile created snakes and the iguana. The goat, Budi, brought forth all the horned animals, the scarab all insects, and Yo Bumba, all fish.
Three of Mbombo's sons then said they would finish creating the world. The first to try, Nyonye Ngana, vomited white ants, but died after. To honor him, the ants went deep in the earth for dark soil to bury him and transformed the barren sands at the earth's surface. The second, Chonganda, created the first plant, which in turn gave rise to all trees, grasses and flowers. And Chedi Bumba, the third son, made the last bird, the kite.
Tsetse Bumba caused trouble on the earth so Mbombo chased him into the sky where he became the thunderbolt. This left people without fire, so Mbombo showed them how to make it from trees. Once the creation was complete and peaceful, Mbombo delivered it to mankind and retreated into the heavens, leaving Loko Yima to serve as "god upon the earth". The woman of the waters, Nchienge, lived in the East, and her son, Woto, became the first king of the Kuba.

The Maasai of Kenya in their creation narrative recount the origin of humanity to be fashioned by the Creator Enkai from a single tree or leg which split into three pieces. To the first father of the Maasai, he gave a stick. To the first father of the Kikuyu, he gave a hoe. To the first father of the Kamba, he gave a bow and arrow. Each son survived in the wild. The first father of the Maasai used his stick to herd animals. The first father of the Kikuyu used his hoe to cultivate the ground. The first father of the Kamba used his bow and arrow to hunt.
Although Maasai people have also converted to Christianity, many still practice their traditional religion. The Maasai believe that he is the god of the sun, love and was the creator of the world; in another one of their traditions, this god married Olapa (the goddess of the moon).

They were then given the ability to see and taste their food. Finally, they were given speech and hearing with which to entertain oneself ("An African Story"). This shows the value system at work among the Shilluk, that work comes above all else. It also attempts to explain the differences between men of various races by telling of how they came about.
A West African creation tale explains how two spirit people were accidentally sent down to earth by the sky god. Lonely, the people decided to create children from clay, but feel they must hide them when the sky god comes down. Because they are hidden in fire, the children soon turn to various shades based on how long they had been exposed to the heat. Over time, these clay children grow up and move to various regions of the earth, ultimately populating it (Fader). Much like that of the Shilluk people, this story serves a two-fold purpose: it explains both the creation of man as well as accounts for the differences among him. This tale shows the West Africans value these differences because they feel that all men are created equal and should be treated as such.

His kingdom is heaven or Xenos "The land of angels and gods of protection". He is said to have created Primus angels Litu and his wife to be guardian angels of Jesus when he was born. He is also said to have created the archangels, including Michael, Uriel, and Gabriel. He also created Eden and Eva with Adam. His first angel was Lucifer, the "Devil," whom later wanted to take the kingdom but was banished from heaven with a few other angels.
The creation stories of uNkulunkulu tell that he came from the reeds, and from them he brought forth the people and the cattle. He created everything, from land and water to man and the animals. He is considered the first man as well as the parent of all people. He taught the Zulu how to hunt, how to make fire, and how to grow food.[

Mwuetsi objected and said he wished to live on the land. Maori reluctantly agreed, but said Mwuetsi would give up immortality if he did. After a while Mwuetsi complained of loneliness, so Maori sent him a woman, Massassi (the morning star), to keep him company for two years.
Each night they slept on opposite sides of a campfire, until one night Mwuetsi jumped over the flame and touched Massassi with a finger he had moistened with the ngona oil. In the moning Massassi was huge, and soon gave birth to plants and trees until the whole earth was covered by them.
At the end of two years Maori took Massassi away. Mwuetsi wept for eight years, at which time Maori sent him another woman, Morongo (the evening star), saying that she could stay for two years. On the first night Mwuetsi touched her with his oiled finger, but she said she was different than Massassi, and that they would have to oil their loins and have intercourse. This they did, this night, and every night thereafter.
Every morning Morongo gave birth to the animals of creation. Then she gave birth to human boys and girls, who became full-grown by that very same evening. Maori voiced his displeasure with a fierce storm, and told Mwuetsi he was hastening his death with all this procreation.
Morongo, ever the temptress, instructed Mwuetsi to build a door to their habitat so that Maori could not see what they were doing. He did this, and again they slept together. Now in the morning Morongo gave birth to violent animals; snakes, scorpions, lions, etc. One night Morongo told Mwuetsi to have intercourse with his daughters, which he did, thereby fathering the human race.

According to Yoruba mythology, the first Yoruba kings were the offspring of the creator, Oduduwa (oh-doo-doo-wah). A Yoruba king's crown identifies the status of its wearer and gives the king the power to interact with the spirit world in order to benefit his people. A veil, a large face, and a group of birds are commonly appear on a Yoruba king's crown.
Long, long ago, Olorun (OH-low-run), the sky god, lowered a great chain from the heavens to the ancient waters. Down this chain climbed Oduduwa, Olorun's son. Oduduwa brought with him a handful of dirt, a special five-toed chicken, and a palm nut. He threw the dirt upon the ancient waters and set the chicken on the dirt. The chicken busily scratched and scattered the dirt until it formed the first dry earth. In the center of this new world, Oduduwa created the magnificent Ife (EE-fay) kingdom. He planted the palm nut, which grew into a proud tree with 16 branches, symbolizing the 16 sons and grandsons of Oduduwa.
Oduduwa was the first ruler of the kingdom and the father of all Yoruba. Over time he crowned his 16 sons and grandsons and sent them off to establish their own great Yoruba kingdoms. As descendants of the sky god, these first Yoruba rulers and their direct descendants were divine kings. Only they could wear special veiled crowns that symbolized their sacred power.
Yoruba Wikipedia



No comments:
Post a Comment